For nearly two centuries, the railroad industry has relied on wood ties as the foundation of our rail infrastructure. What began with naturally resilient, centuries-old hardwood has evolved into chemically-treated wood that struggles to meet modern performance demands. As a result, the railroad industry now faces a critical choice: continue with traditional practices that lead to premature tie failures and environmental harm or embrace sustainable solutions that will serve future generations.
Each year, North American railroads replace approximately 22 million wood ties—equivalent to around 6 million trees. More concerning is that 4–6 million of these ties are being replaced in less than 12 years, far shorter than their expected service life. And this accelerated replacement cycle stems from a fundamental problem: We’ve harvested all the old-growth trees, leaving only new-growth wood that simply isn’t fit for purpose, even when treated with creosote.
The shift toward sustainable railroad infrastructure isn’t just an environmental nicety—it’s an operational necessity that will reshape the legacy we leave for our children and grandchildren. The decisions the railroad industry makes today will determine whether the next generation inherits a transportation system that continues to deplete natural resources or one that demonstrates how creative problem-solving can turn waste into lasting infrastructure.
Environmental Impact: The Legacy of a Cleaner Planet for Our Kids

The environmental benefits of sustainable railroad infrastructure will extend far beyond our lifetime. By adopting composite ties made from recycled plastic, the railroad industry can dramatically reduce its environmental footprint in several key areas:
Reduction in Deforestation
With approximately 3,250 wood ties used per mile across the 140,000 freight miles of railroad tracks connecting North America, the demand for mature hardwood is immense. And traditional railroad infrastructure requires continuous harvesting of trees, threatening forest ecosystems that future generations will need for climate stability and biodiversity.
At Evertrak, our annual production rate of 1 million composite ties eliminates the need to cut down 250,000 mature trees. Scaled to industry levels, adopting sustainable railroad ties could save millions of trees annually, preserving forests as carbon sinks and wildlife habitats for our children’s future.
Elimination of Toxic Chemical Treatments
Approximately 98% of wooden railroad ties are coated in creosote, a known carcinogen that poses serious health and environmental risks. While creosote extends the life of wood ties, it doesn’t prevent eventual rotting and introduces harmful substances into soil and groundwater that can persist for generations.
Evertrak’s Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) ties eliminate the need for these toxic preservatives, preventing the release of these toxic hazardous chemicals into the environment each year. This means future generations won’t have to deal with the long-term health and environmental consequences of today’s chemical treatments.
Plastic Waste Reduction
Today, only 9% of the planet’s plastic waste is effectively recycled. By repurposing existing plastic into railroad infrastructure, our team at Evertrak creates a meaningful solution for plastic pollution while building lasting value.
Our production of 1 million Evertrak ties annually sequesters 180 million pounds of plastic from landfill. At industry scale, replacing just the prematurely failing wood ties (4–6 million annually) with composite alternatives would sequester 720,000,000 pounds or 360,000 tons of plastic each year.
Unlike short-lived consumer applications of recycled plastic, railroad ties sequester this material for decades, creating what we call a “plastic forest” (instead of a wooden one) with residual value for future generations.
Lower Carbon Footprint Through Extended Replacement Cycles
The environmental impact of railroad maintenance extends beyond materials to include the carbon emissions associated with replacement operations. Wood ties in high-decay zones typically last 8–12 years, necessitating frequent replacement work.
Evertrak’s composite ties are engineered to perform reliably for 50 years—up to five times longer than wood ties in challenging environments. This longevity significantly reduces the carbon emissions associated with manufacturing, transporting, and installing replacement ties, helping to mitigate climate change impacts that the next generation will otherwise face.
Economic Inheritance: Jobs and Growth in Modern Railroad Advancements
The green rail technology revolution isn’t just about environmental benefits—it will create substantial economic opportunities that today’s youth will inherit as they enter the workforce.
Market Growth and New Industries
The global market for composite railroad ties is projected to grow from $73 billion in 2025 to 220 billion by 2034, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 13% during this period, representing significant growth potential. This expansion will create new business opportunities in manufacturing, materials science, and recycling technologies that don’t exist at scale today.
These aren’t just temporary jobs we’re talking about; they’re the foundation of sustainable industries that will provide career paths for decades to come. Young people today may find themselves working in advanced materials manufacturing, recycled plastic processing, or specialized railroad engineering—fields that are being expanded by today’s railroad sustainability initiatives.
Creation of Skilled Manufacturing Jobs
The transition to composite railroad ties requires specialized manufacturing processes that create higher-skilled, better-paying jobs compared to traditional wood tie production. At Evertrak, we’re proud to operate our AAR M-1003 certified manufacturing facilities that employ skilled workers in the production of GFRP ties.
As demand grows for eco-friendly rail solutions, so will the need for workers skilled in composite manufacturing. The next generation will benefit from these employment opportunities that combine traditional manufacturing with advanced materials science.
Economic Benefits to Communities
Sustainable railroad infrastructure manufacturing facilities provide stable employment and contribute to local tax bases. Unlike the boom-and-bust cycles associated with resource extraction industries, manufacturing based on recycled materials offers sustainable economic development for communities.
The ripple effects extend beyond direct employment to include supply chains and vendor relationships, transportation services, and the local service economy. Communities hosting these facilities will enjoy economic resilience that grows alongside innovations in green infrastructure.
Infrastructure Built to Last: Reliability for Tomorrow
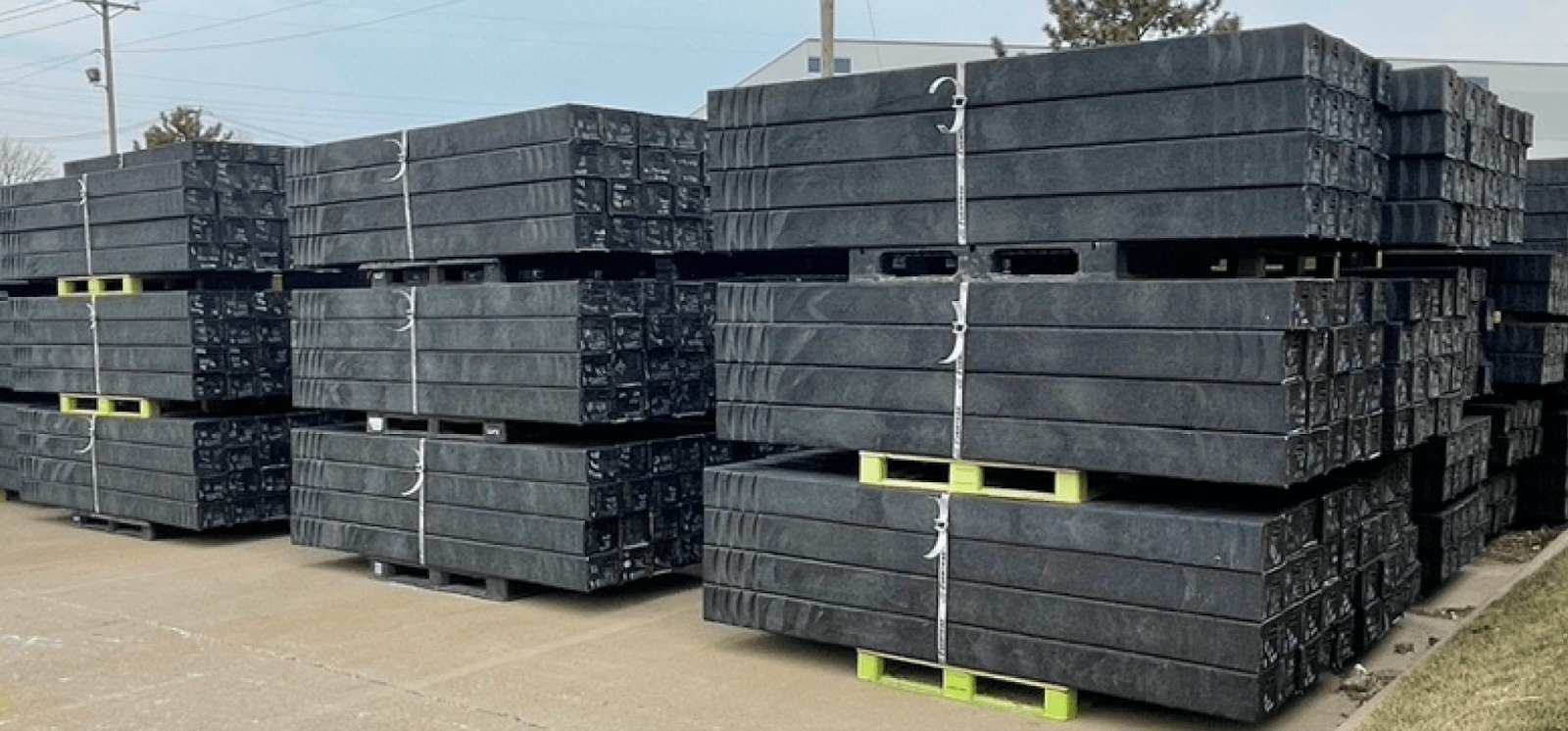

One of the most significant benefits the next generation will inherit from today’s sustainable railroad choices is infrastructure designed for longevity and performance.
Extended Service Life
The dramatic extension of service life between an Evertrak 7000 tie and wood ties means the infrastructure investments made today will still be serving communities when today’s children are running the railroad industry.
This longevity isn’t theoretical—our ties are in service with Class I railroads today, proving their durability in real-world conditions.
Reduced Maintenance Requirements
The frequent replacement of wood ties creates significant operational disruptions and maintenance costs for railroads. These disruptions affect service reliability and divert resources from other needs. By extending the replacement cycle through sustainable railroad ties, future generations will inherit a rail system with more predictable maintenance needs and fewer service interruptions.
This reliability is particularly important as future transportation demands increase. The Federal Highway Administration (FHA) predicts total U.S. freight activity will grow by 50% in tonnage, reaching 28.7 billion tons, and $36.2 trillion between 2020 and 2050. A sustainable railroad infrastructure will be better positioned to dip into trucking’s monopoly on the market to handle this growth efficiently.
Climate Change and Consistency Across Environmental Conditions
Climate change will likely bring more extreme weather conditions in the coming decades. Traditional wood ties are particularly vulnerable to moisture and temperature fluctuations, leading to even higher rates of premature failure in challenging environments.
Evertrak’s composite ties maintain consistent performance properties under extreme environmental conditions. This stability will become increasingly valuable as future generations deal with more unpredictable climate patterns that would otherwise accelerate the deterioration of traditional infrastructure.
Long-term Cost Benefits for American Railroads
The economic calculations for infrastructure decisions must consider future generations. While the initial investment in sustainable railroad ties may be higher than wood alternatives, the total cost of ownership over time strongly favors composite solutions—especially in high-decay zones where replacement cycles are accelerated.
When factoring in labor, materials, and operational disruptions, the extended service life of composite ties translates to significant cost savings over time. These savings represent resources that future generations won’t have to spend on premature infrastructure replacement, allowing those funds to be directed toward other transportation needs.
Innovation Pipeline: Setting the Stage for Future Advancements

The benefits of sustainable railroad infrastructure extend beyond the direct advantages of today’s technology to include the innovation pathways they open for the future.
Potential for Smart Infrastructure
As composite materials become the new standard for railroad ties, they create opportunities for embedding sensors and monitoring technologies directly into the infrastructure. These “smart ties” could provide real-time data on track conditions, allowing for predictive maintenance and improved safety.
Future generations may inherit a railroad network that monitors itself, identifying potential issues before they become problems and optimizing maintenance schedules automatically. This intelligent infrastructure represents a fundamental shift from the reactive maintenance approach necessitated by unpredictable wood tie deterioration.
Material Science Advancements
The development of high-performance composite railroad ties drives continuous innovation in materials science. The requirements for strength, durability, and resilience in railroad applications push the boundaries of what’s possible with recycled materials.
These advancements won’t be limited to railroad applications. The next generation will benefit from cross-industry applications of these technologies in construction, automotive manufacturing, and other infrastructure sectors. Today’s railroad innovation becomes tomorrow’s platform for broader sustainable material solutions.
Industry Partnerships Driving Continuous Improvement
Evertrak works closely with major railroads and material suppliers to continuously improve our products. These collaborative relationships create an innovation ecosystem that will benefit the next generation through increasingly advanced sustainable infrastructure solutions.
With transportation and railroad industries shifting toward sustainability, market demand will attract research investment, driving a cycle of improvement that will continue to yield benefits for decades. Future generations will inherit not just today’s solutions but the accelerated innovation trajectory they enable.
Educational Impact: Inspiring the Next Generation

The transformation of railroad infrastructure through sustainable materials and practices provides powerful real-world examples that can inspire and educate young people about environmental solutions at scale.
Demonstrating Circular Economy Principles
The railroad industry’s adoption of ties made from recycled plastic demonstrates circular economy principles in action. The railroad industry transforms waste materials into critical infrastructure that lasts for decades, proving circular economy principles in action.
This tangible demonstration helps young people understand that sustainability isn’t just about small consumer choices—it can include industrial-scale solutions that transform waste streams into valuable assets. The railroad becomes a visible, compelling example of circular economy principles that future leaders can expand upon.
STEM Education Opportunities
The development and deployment of composite railroad ties combines engineering, materials science, environmental science, and logistics—creating rich educational opportunities for students interested in STEM fields. Schools near railroad infrastructure can use this real-world application to illustrate scientific principles and engineering challenges.
Evertrak supports educational initiatives that connect students with the science behind sustainable infrastructure. By engaging with schools and universities, our industry can help prepare the next generation of engineers and scientists who will further advance sustainable transportation solutions.
Shaping Future Career Aspirations
Young people today seek meaningful work that tackles environmental challenges. The transformation of railroad infrastructure through recycled materials provides a visible example of how traditional industries can innovate toward sustainability, potentially attracting talented young people to careers in the railway sector who might otherwise look elsewhere.
This influx of sustainability-minded talent will accelerate innovation and ensure that railroad freight transport continues to adopt and push for environmental responsibility long after today’s decisions are made. Plus, working along a vast rail network spread across the country means young people can find these green-sector jobs closer to home as opposed to coastal cities currently dominating the field.
The Balance Sheet for Future Generations
When we evaluate the full impact of sustainable railroad infrastructure on future generations, we must consider both quantifiable benefits and broader societal value.
Total Cost of Ownership
The financial equation strongly favors sustainable railroad ties over time. Wood ties that fail prematurely create not just replacement costs but also operational disruptions that cascade through the transportation system. By investing in ties with 50-year service lives, we dramatically reduce the lifetime costs that future generations will bear.
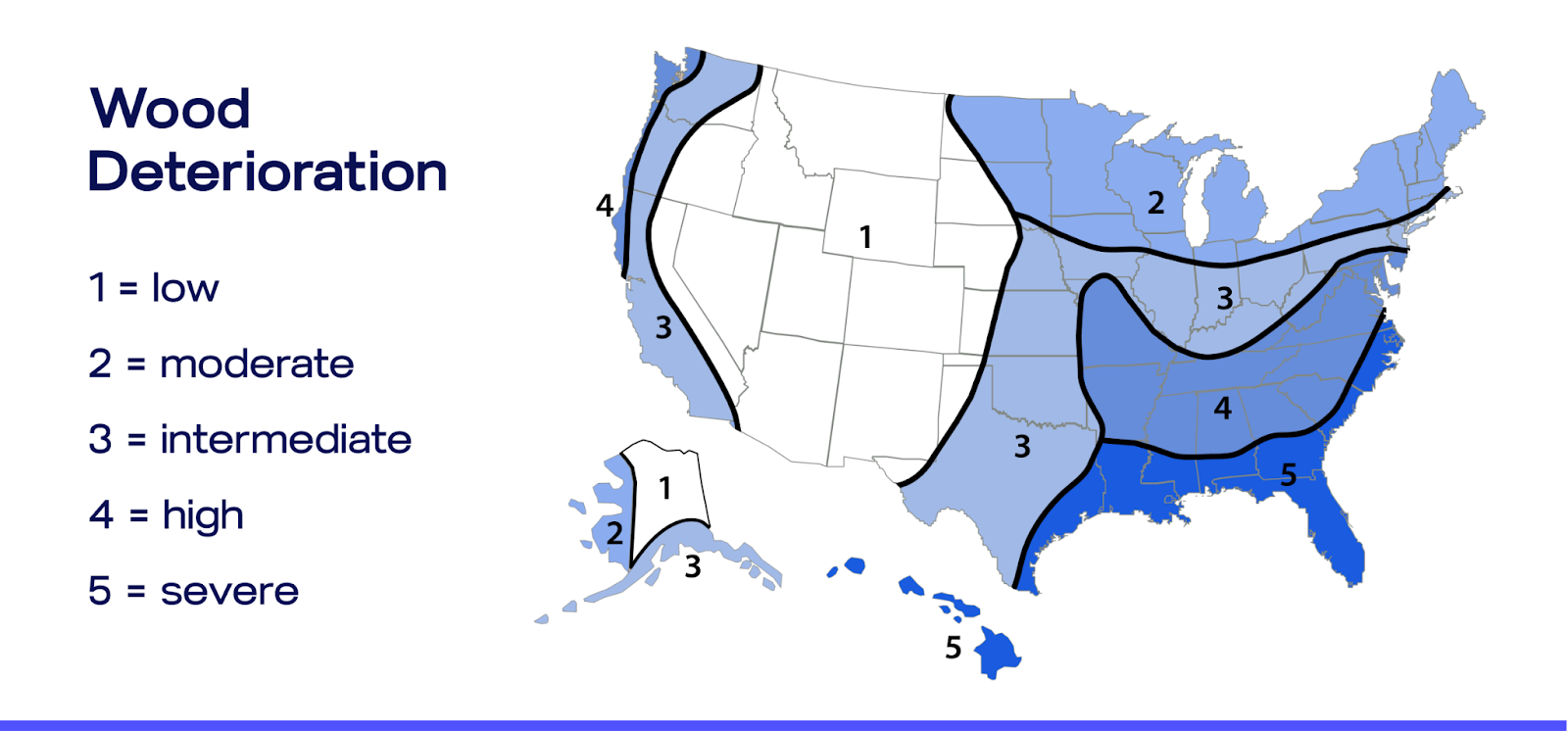
For railroads operating in high-decay zones (Deterioration Hazard Zones 4 and 5), the economic case is particularly compelling. Wood ties in these areas may last only 5 years, creating a replacement cycle that burdens future maintenance budgets and diverts resources from other needs.
Environmental Return on Investment
The environmental ROI extends far beyond the direct benefits of reduced deforestation and plastic waste. By creating demand for recycled plastic, sustainable railroad ties help establish collection systems and processing capabilities that benefit other industries.
Additionally, the carbon sequestration benefits of both preserved forests and long-term plastic sequestration represent environmental assets that appreciate over time. Future generations inherit not just the ties themselves but the positive environmental impacts that compound through the decades.
Social Benefits of Fuel Efficient Transportation
Railroad transportation is already one of the most efficient modes of freight movement, with rail cars moving one ton of freight 500 miles on a single gallon of diesel fuel—roughly four times more efficient than trucks. By ensuring freight railroad infrastructure remains one of the most reliable and cost-effective transport modes through sustainable practices, we preserve this efficiency advantage for future generations.
This efficiency translates to reduced emissions, lower transportation costs, and less congestion on highways. These benefits extend throughout the economy, affecting everything from consumer goods prices to air quality in communities near transportation corridors, making rail transport the obvious choice for developing a more sustainable future.
Laying Tracks to a Better Tomorrow: The Role of Railroads in Sustainable Infrastructure
The decisions made today about railroad infrastructure will echo for generations. By choosing to promote sustainability in the rail sector through solutions like Evertrak’s composite ties, the railroad industry can transform from a consumer of resources to a utilizer of waste streams, creating infrastructure that serves both present needs and future generations.
The sustainable railroads of 2030, 2040, 2050, and beyond will look fundamentally different from today’s system—not just in the materials used but in the entire approach to infrastructure lifecycle management. Ties made from recycled materials that last for decades, potentially embedded with monitoring technology, will form the foundation of a transportation network that operates with greater predictability and efficiency than today’s rails.
This vision isn’t a distant future—it’s taking shape today through the choices of forward-thinking railroads that embrace the operational and environmental benefits of sustainable infrastructure. At Evertrak, we are driving this transformation by delivering high-performance solutions that outperform traditional alternatives while maximizing environmental benefits.
The railroad industry has always connected communities and enabled economic growth. Now, through sustainable practices, it can connect generations—building infrastructure today that will serve our children and grandchildren while demonstrating how traditional industries can lead in creating environmental solutions.
Every Evertrak tie installed represents not just an improvement in today’s railroad operations but an investment in the world we leave to future generations—one with more trees, less plastic pollution, fewer toxic chemicals, and more reliable infrastructure. If you ask us, that’s a legacy worth building, one tie at a time.




